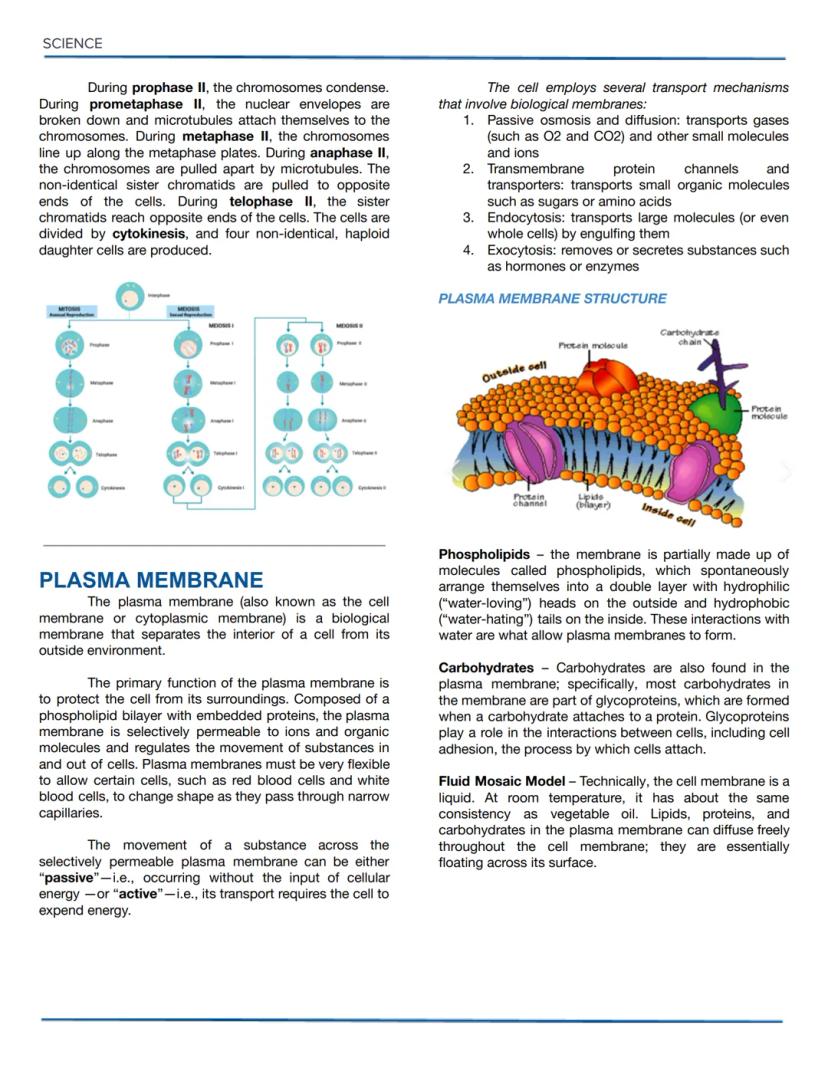
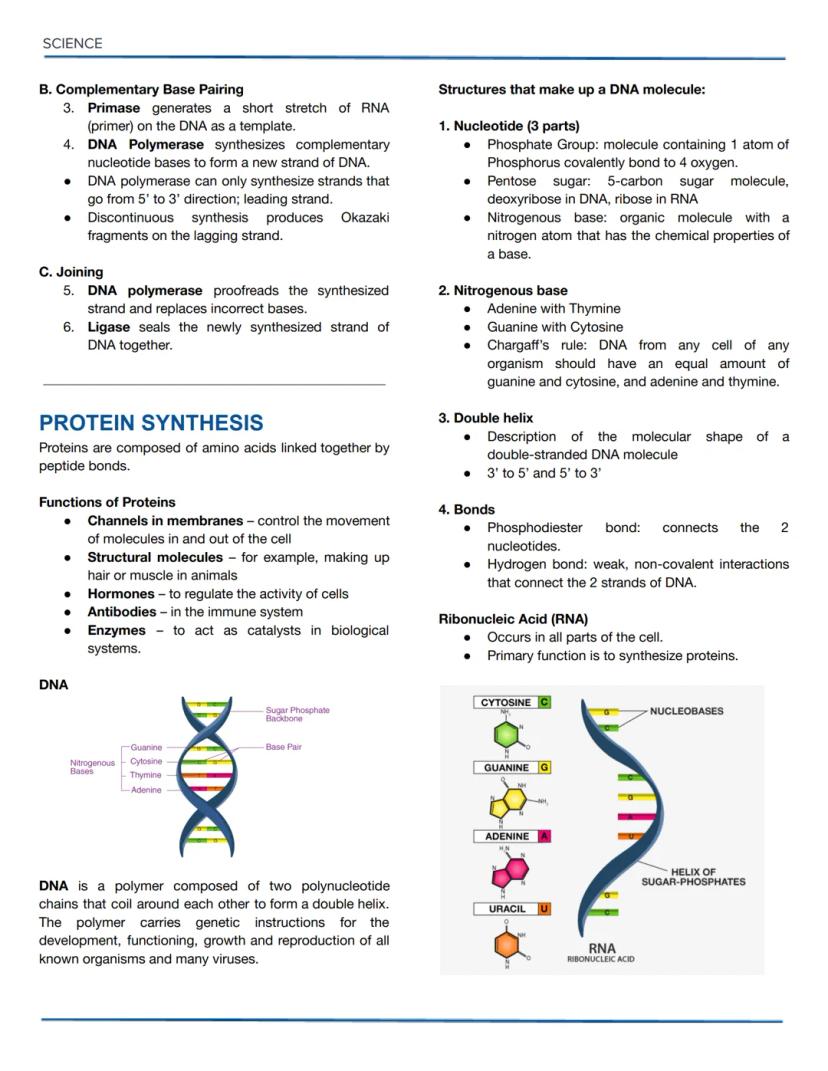
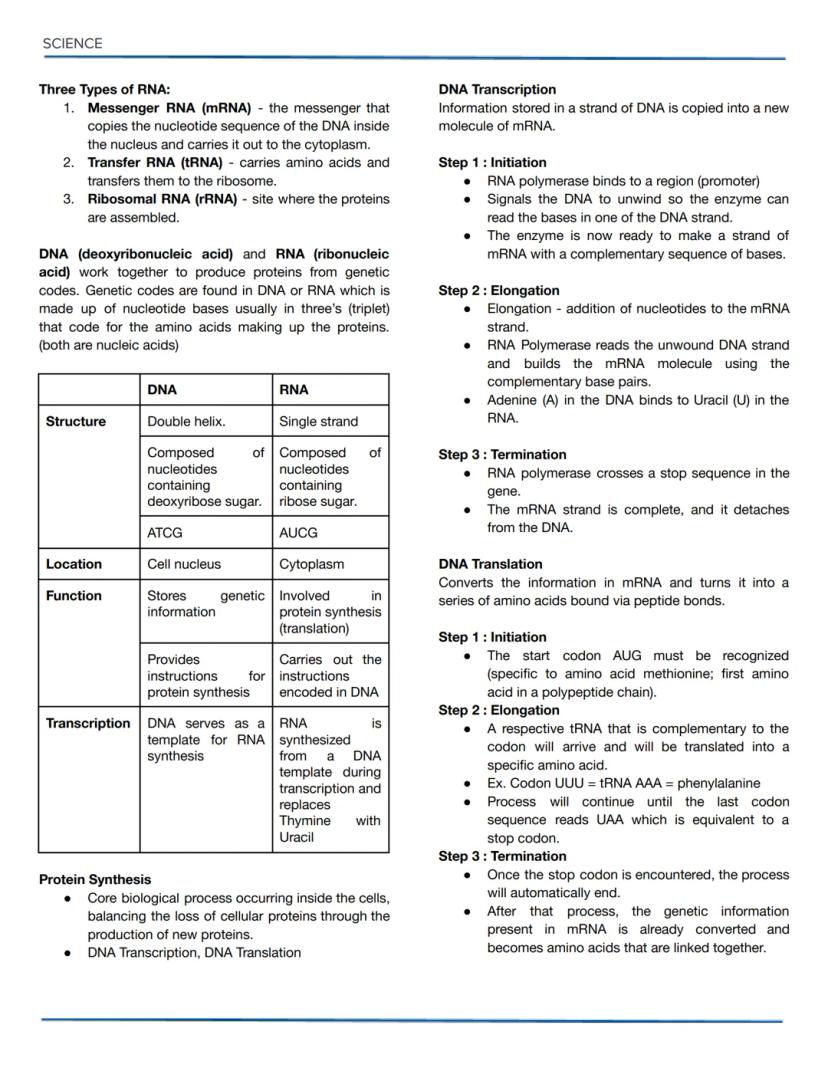
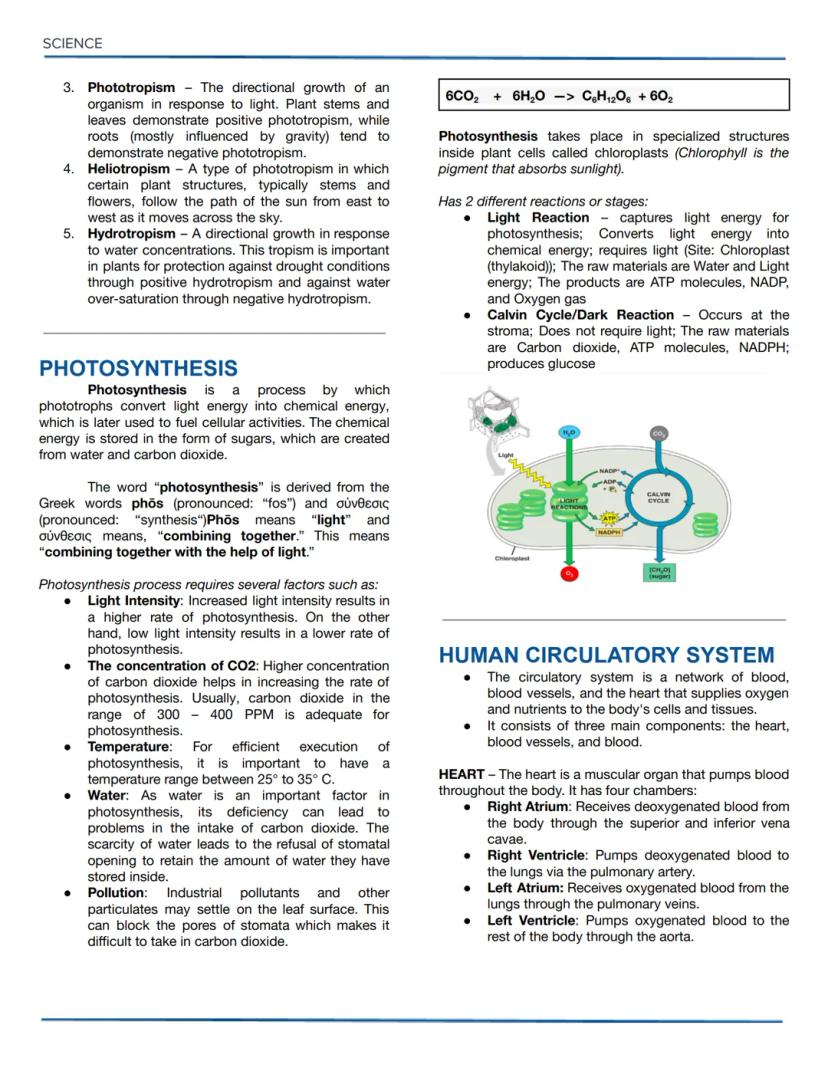
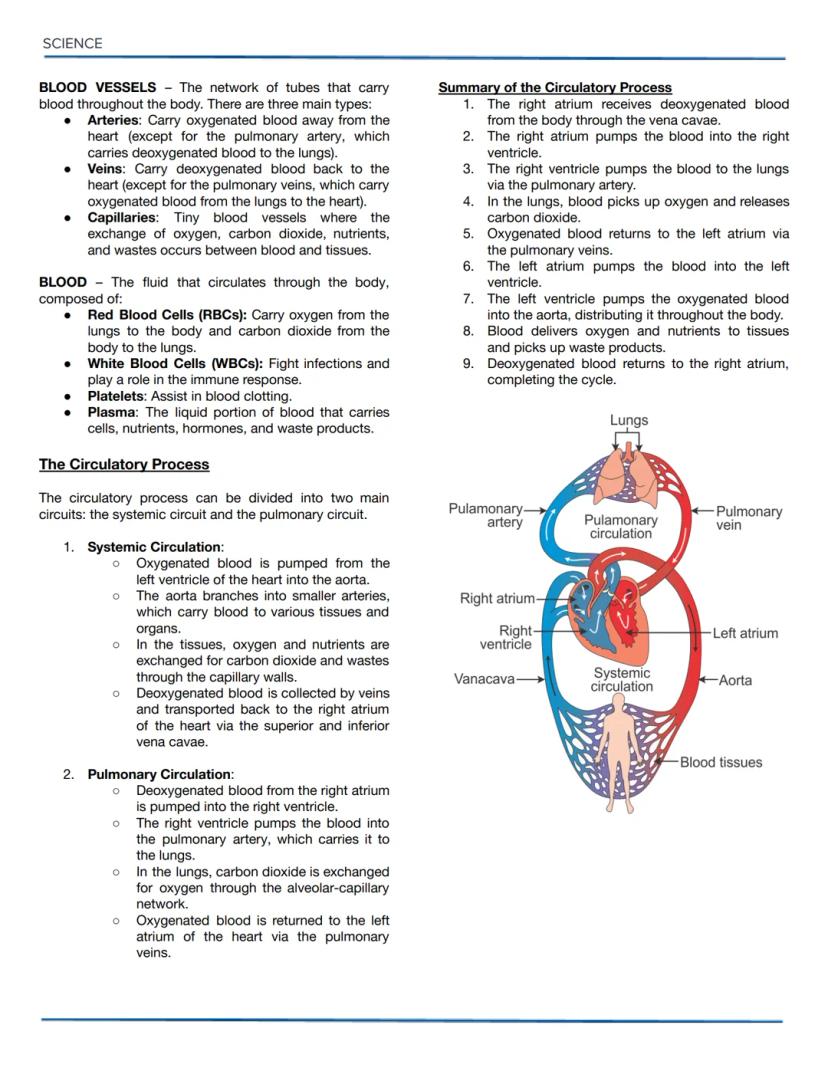
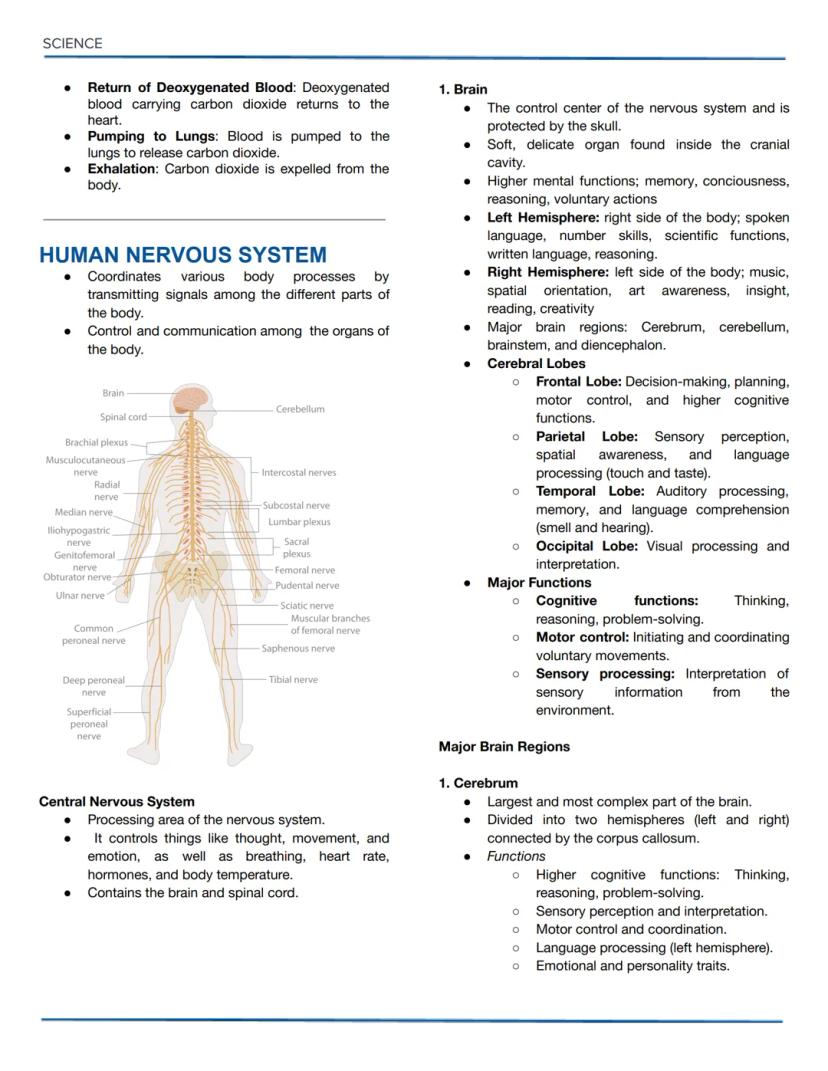
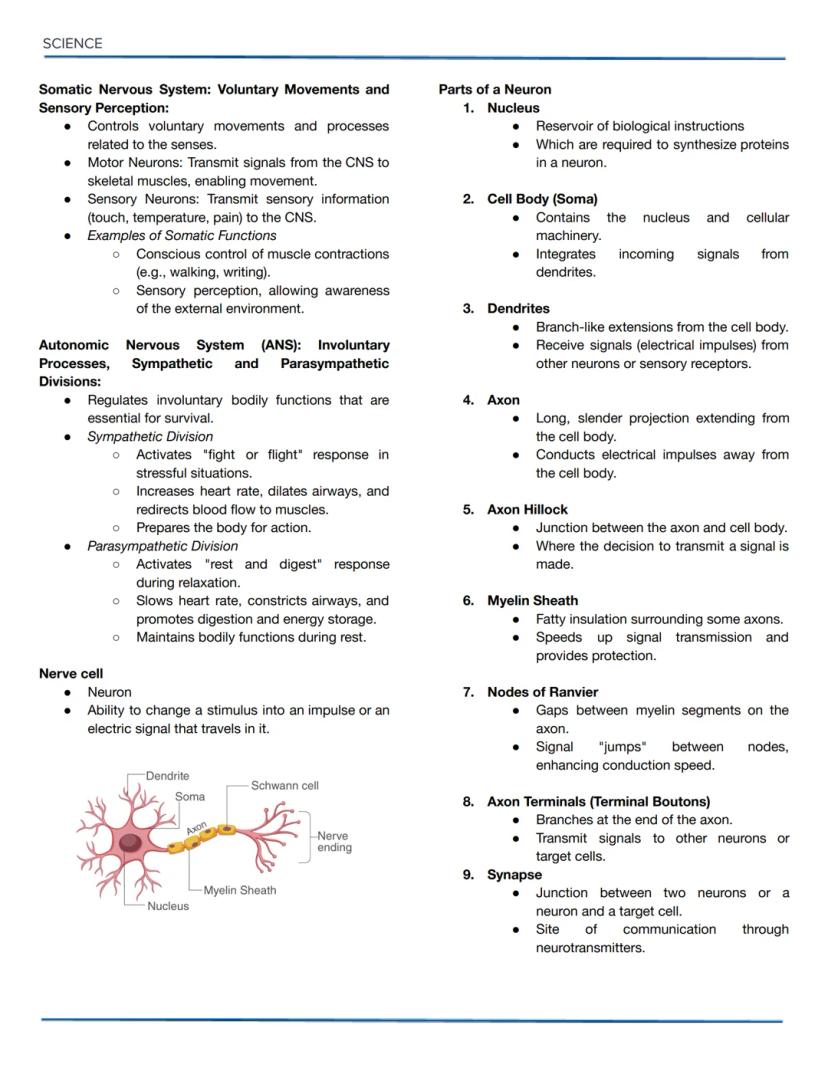
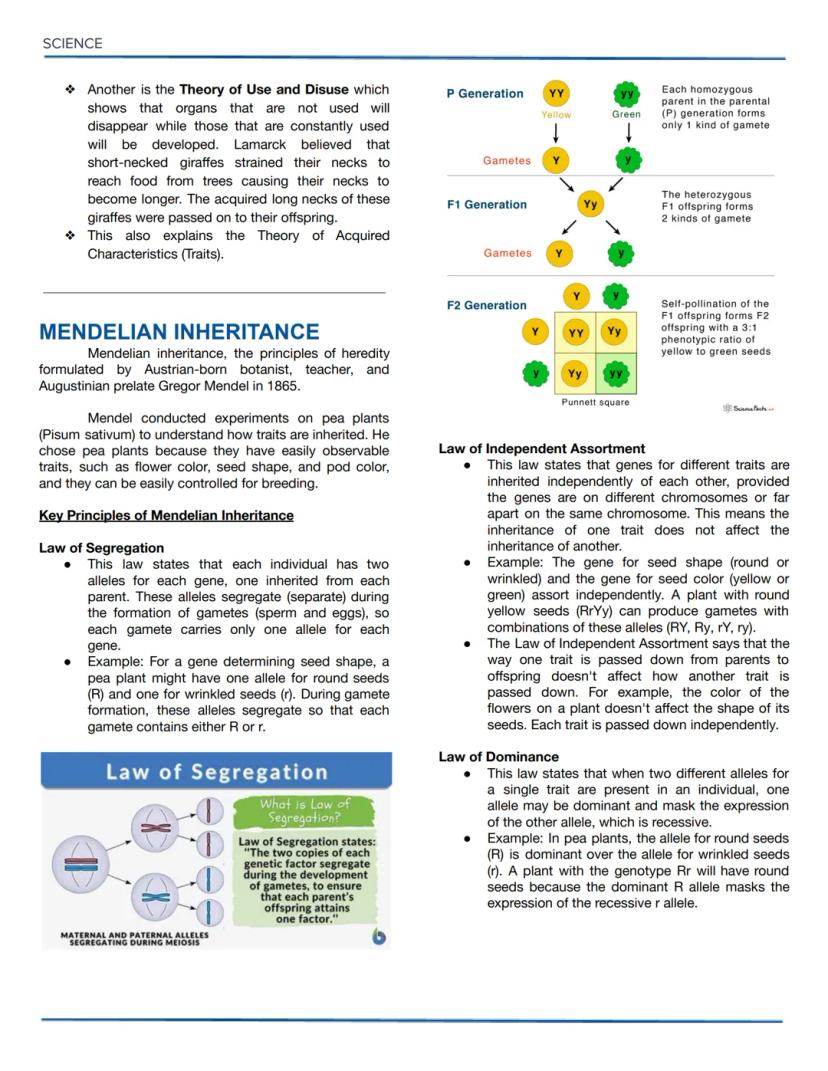
Osmotic Solutions and DNA Replication
Osmosis moves water across membranes to balance concentrations. In isotonic solutions, water moves equally in both directions. Hypotonic solutions have less solute outside the cell, so water rushes in and cells swell. Hypertonic solutions have more solute outside, pulling water out and shrinking cells.
DNA replication is a semiconservative process where each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one new strand. Key enzymes work together like a construction crew: helicase unwinds the double helix, primase adds starting points, DNA polymerase builds new strands, and ligase seals everything together.
The process has three main steps: unwinding and unzipping the DNA, adding complementary base pairs (A with T, G with C), and joining the new strands. DNA polymerase can only work in the 5' to 3' direction, creating Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
Remember: DNA replication is like unzipping a jacket and making two identical jackets from the original pieces!